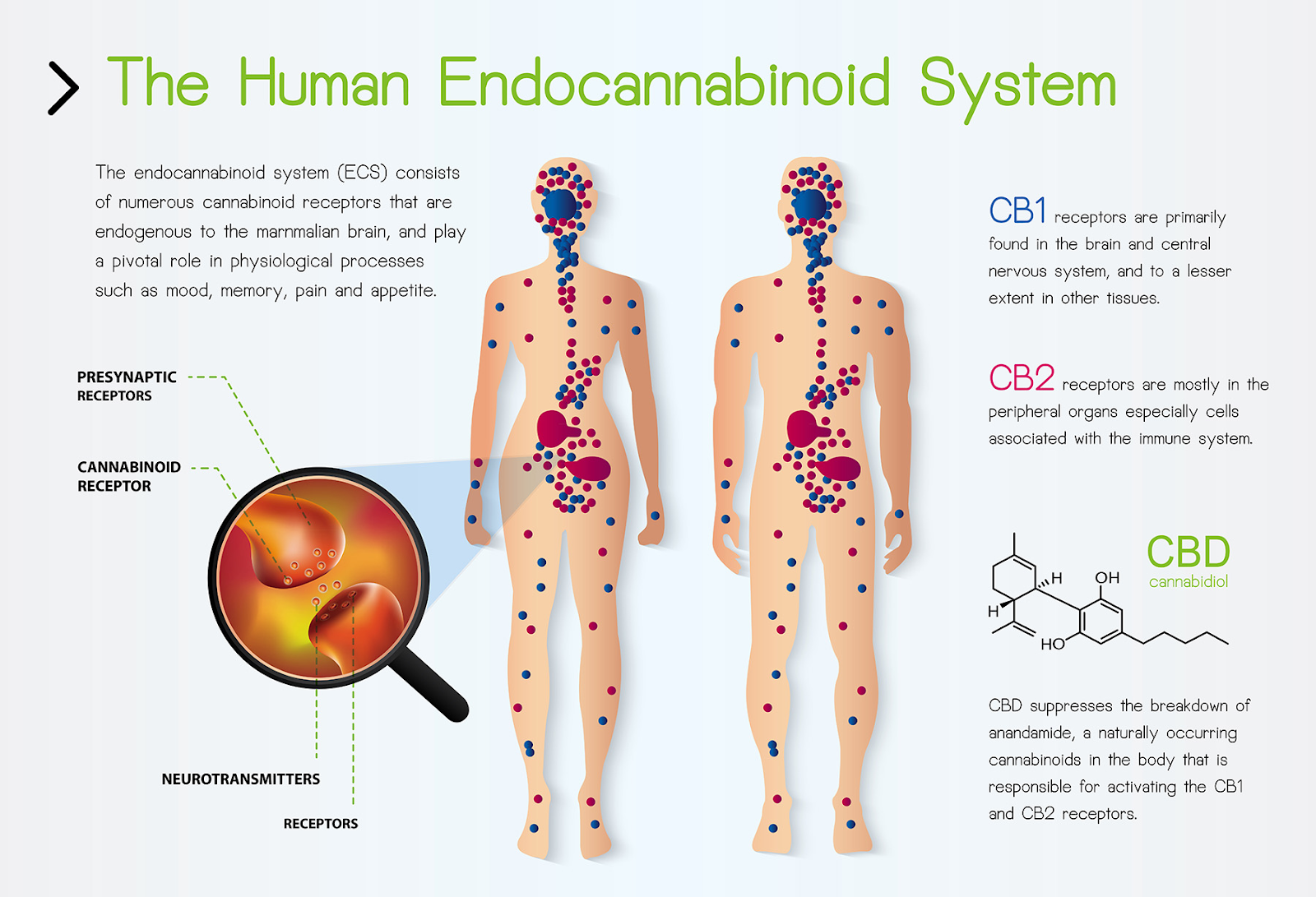
The Endocannabinoid System, or the ECS, is a complex system found in every single body (including pets!) – even if you don’t use cannabis.
The ECS is made up of three main components and plays a role in regulating many different physiological processes such as mood, memory, appetite, pain, sleep, and more!
- Endocannabinoids which are produced by the body (similar to cannabinoids) act as neurotransmitters that help regulate the activity of the ECS. They are present in various organs and tissues, such as the muscle, brain, and circulating cells, and become active when they bind with a cannabinoid receptor.
- Cannabinoid Receptors which are proteins found on cell surfaces that cannabinoids bind to and send signals. Found throughout the body, but mostly in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Currently, we know most about CB1 & CB2 receptors:
- CB1 – These exist mostly in the brain and central nervous system. These act like traffic control; adjusting the levels and activity of most of the other neurotransmitters.
- CB2 – These exist mostly in the immune tissues and are crucial to our immune functions.
- Enzymes that break down cannabinoids.
How does it work?
When endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors, they activate and trigger a series of chemical reactions that can affect various physiological processes.
As a reminder, the ECS is involved in many different physiological processes, including the regulation of appetite, pain, mood, sleep, and immune system function.
Why is it important for our health?
The ECS is a complex system that is still being studied, but research has shown that it can play a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis or balance in the body. When the ECS is not functioning properly, it can lead to a range of health problems, such as chronic pain, inflammation, and neurological disorders. Pertwee, R. G. (2006).
As an analogy, the ECS can be likened to a skilled orchestra conductor. In an orchestra, the conductor’s role is to regulate the tempo, volume, and coordination of each instrument to ensure harmonious music. Similarly, the ECS acts as a conductor within the body, orchestrating various physiological processes. Just as the conductor communicates with different sections of the orchestra to maintain harmony, the ECS communicates with different systems in the body to maintain homeostasis. When the ECS is in tune and functioning properly, the body operates smoothly like a well-coordinated symphony.


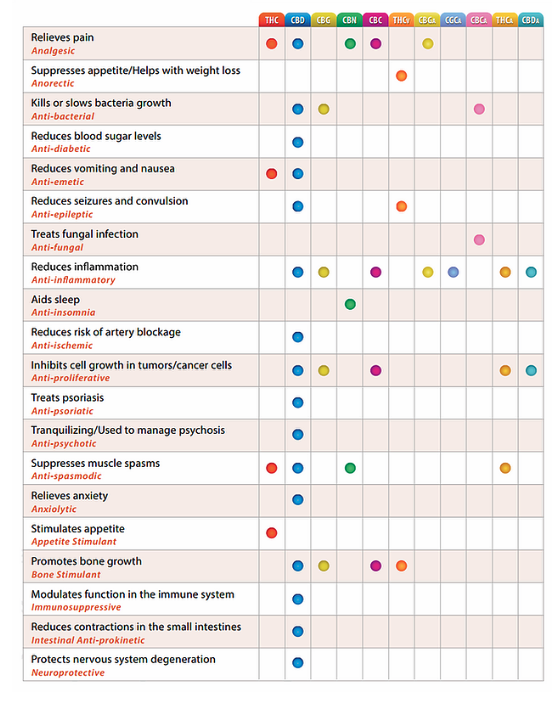
Furthermore, cannabinoids found in the marijuana plant can interact with the ECS, altering neurotransmitter release and producing various effects on the body, including relaxation and euphoria.
Cannabinoids may promote sleep in those who struggle with it, reduce pain for those with chronic inflammation, and instill calm in those with anxiety.
- Two of the most commonly known cannabinoids are THC & CBD.
- Opioids are lab-made & cannabis is nature made. Your body was meant for cannabis!
Pertwee, R. G. (2006). The pharmacology of cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: an overview. International journal of obesity, 30(Suppl 1), S13-S18. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.ijo.0803272]






